|
MySQL is a popular database management system. It allows
you to add, access, and process stored data. This document will guide you through:
Creating MySQL Database and Its Users
MySQL users cannot exist separately from MySQL databases.
You must stick to the following sequence:
- Create a database
- Add MySQL users to each created database.
However, MySQL users can be shared by different databases.
To create a MySQL database, do the following:
- Select MySQL in the Databases menu and
MySQL DB creation Wizard automatically appears.
- On the form that shows enter the name of the database
and database description if needed:
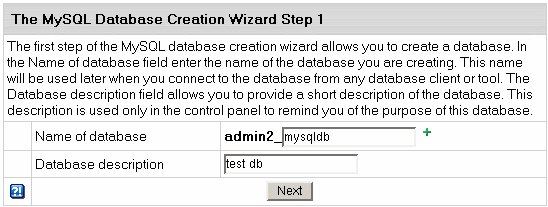
NOTE:
Starting from version 2.3.1, new MySQL databases are created
with the username_ prefix, where username is a unique identifier that
contains either first letters of the name of an account under which this database is created,
or that account name's first letters and a unique number if there are several account names starting
with the same letters. This is done to prevent the creation
of databases with the same name under different users.
- Agree with additional charges if any.
- In the form that appears, create a new user or grant privileges to users of other databases:
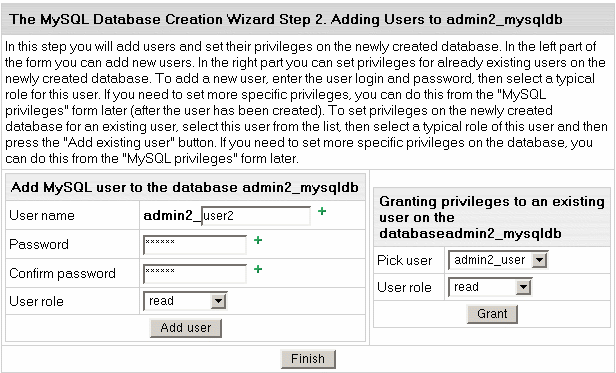
- Add a new user to the database you have just created.
User roles are explained below. Click
Add user.
- Choose roles for users of other databases so they can
use your new database. Click Grant.
- Click Finish to complete creating your MySQL database.
Editing MySQL databases (phpMyAdmin)
You can edit the content of your databases using the phpMyAdmin utility
that comes with your control panel. To run phpMyAdmin, do the following:
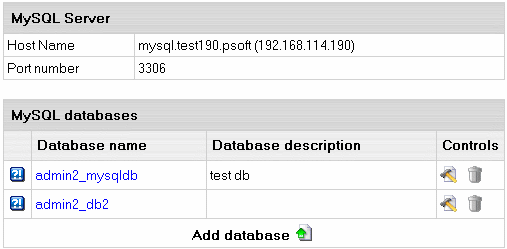
- Select MySQL DBs in the Databases menu.
- In the form that appears, click the name of the existing
MySQL Database you want to edit or the Edit icon on its right:
- In the form that appears, click Built in phpMyAdmin
control panel to start editing your database:
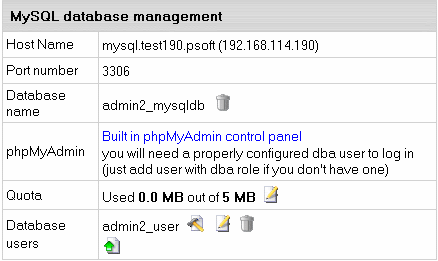
- Follow the instructions of the phpMyAdmin control panel to edit your MySQL DB.
Changing MySQL disk quota.
MySQL disk quota is the maximum allowed size of one
MySQL database. If you exceed this quota, you'll be charged
for overlimit at a different (usually higher) price.
To change MySQL disk quota, do the following:
- Select MySQL DBs in the Databases menu.
- Click the MySQL Database or the Edit icon on its right:
- Click the Change button against the Quota field and enter the new quota:
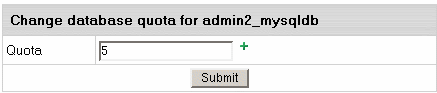
- Click Submit.
- Agree to additional charges.
Changing user passwords.
To change user password in the MySQL database, do the following:
- Select MySQL DBs in the Databases menu.
- Click the MySQL Database or the Edit icon on its right:
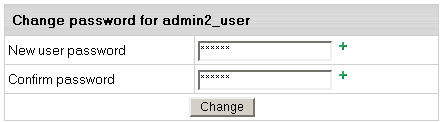
- On the MySQL database management page click the Change password
icon next to the DB user.

- Enter new password and click the Change button.
Adding MySQL users and granting them privileges.
Here you will learn how to add new users to an existing
MySQL database.
- Select MySQL DBs in the Databases menu.
- Click the MySQL Database or the Edit icon on its right:
- On the form that shows, click the Add icon against the Database users field.
- Fill the following form:
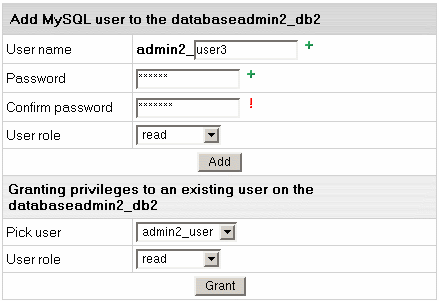
Each user role involves a fixed set of privileges on this specific database:
| Role: |
Set of privileges: |
| read |
select |
| read/write |
select, insert, delete, update |
| dba |
select, insert, update, drop, create,
alter, index |
- Click the Add or Grant button and agree
to additional charges.
- To edit privileges, click the Edit icon next to
the user. You will be brought to the Privilege Maintenance page.
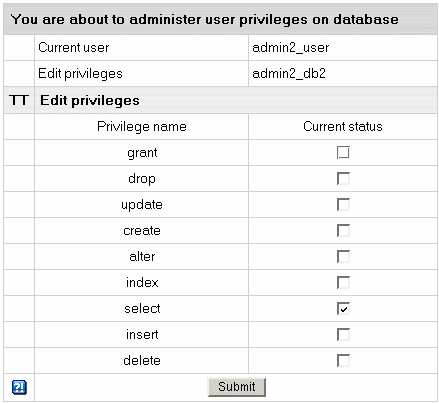
- Check or uncheck the desired privileges and press the Submit button.
Note: For more information on MySQL access privileges, please refer
to www.mysql.com.
Note 2: any changes in user privileges will be applied to the whole selected database.
|